IT Solution
IT is our life
Wednesday, February 15, 2017
Wednesday, January 18, 2017
wifi connecting
Wifi: the key benefits and the basics of how it works
The benefit of wifi is obvious: a wireless internet connection means our devices are not tied to a fixed location within a property. You see, wifi transmits a property's internet connection via special radio signals, allowing us to move around from one room to another, with no interruption to our internet connection.
This is obviously super handy for users of laptops, tablets and mobile devices. Once we're connected to wifi, access to the internet is suddenly so much more convenient and flexible.
Sunny day outside? Why not catch up on your emails whilst sipping a coffee in the garden — with wifi, you can!
The basics of wifi in summary:
Wifi is the wireless technology that all internet-enabled devices use to get online — without messing around with cables.
Home wifi internet is made possible via a wireless router, which is basically a box that transmits and receives wireless signals between an internet connection and internet-enabled devices.
To communicate with a router and connect to wifi, a device must have a wireless adaptor. Most internet-enabled devices today come with a wireless adaptor built in — but older computers may require a plug-in adaptor in order to get online wirelessly
General steps to connect to a wifi network near you
The following steps run through the general steps that anyone needs to take to get connected to the internet via wifi.
Step 1: Locate yourself in a property or public space that has a wireless router. I.e. Somewhere where a wifi signal is being transmitted.
Step 2: Make sure that the device you're going to use is a.) Capable of connecting to the internet and b.) Capable of connecting to wifi.
Step 3: Find out the name of the wifi network that the router in your location is transmitting. That's right, each wifi network has its own unique name. Sometimes this can be a sequence of random numbers and letters if it was set by default on the router — but people often personalise the name of a wifi network to help users identify its owners. E.g. "The Smith Family wifi" or "Fred's Cafe".
Step 4: Once you know the name of the wifi network, use your chosen device to find it. This will vary between devices (depending on whether you're using a Windows or Mac computer, or a mobile device). However, the process for connecting to wifi is broadly similar, following something along the lines of: navigate to wifi settings > turn wifi on > click on the name of your wifi network > click "connect".
Step 5: Many wifi networks are made private, with access restricted via a password. If your chosen wifi network is password protected, at this point it will ask you enter that password. Make sure you have the password at hand, and enter it.
You should now be connected to wifi!
An example of how to set up and connect to wifi at home (using a Windows 7 computer)
What you’ll need:
a wireless router
a Windows 7 computer with a built-in wireless adaptor or a separate adaptor.
Follow these step-by-step instructions to connect to wifi

Step 1: Set up your wireless router - an example of which is on the right - (see How to connect to the internet for instructions). Most internet providers now supply wireless routers as standard. When setting up one, it’s important to provide appropriate security so that your computer can’t be entered by anyone but you. Instructions for this should be supplied with the router, but if in doubt, consult an expert.

Step 2: Check that your computer has a built-in wireless adaptor (see left). Up-to-date laptops generally have one, but most desktop computers don’t.
To check whether there’s a built-in adaptor, follow these steps:
Click the Start button.
Right-click Computer.
Click Properties.
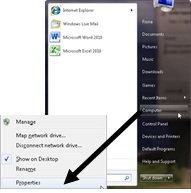
Click Device Manager.
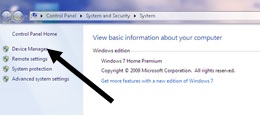
Click the arrow next to ‘Network Adaptors’ to see if there’s a wifi adaptor listed.
If there is a wifi adaptor, a wifi icon should also appear in the system tray in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. In Windows 7,
it looks like the one on the right.
If you don’t have a wireless adaptor, you’ll need to buy one to plug into one of your computer’s USB ports. The adaptor should be supplied complete with instructions on how to use it to connect to a wireless network.
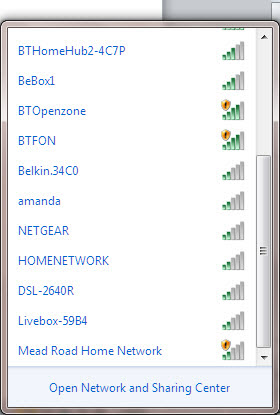
Step 3: To connect to a wireless network, click the wifi icon. You should now see a list of available networks – an example is on the left.
Step 4: To connect to a network, just click on its name. If it’s a secure network and it’s the first time you’ve used it, you’ll need a password. If it’s your home network, your internet provider will have given you a password – sometimes it’s printed on a sticker attached to the router.
If you’ll be using the same connection regularly, you can tick the box to connect automatically.
Step 5: The first time you connect to a network, you’ll be asked to choose whether it’s a home, work or public network.
Warning: Be very careful if you connect to unsecured wireless networks such as wifi ‘hotspots’ in public places. While on them, it’s important not to use websites that require you to enter personal or financial details as other users of the network could gain access to these details.
Monday, January 16, 2017
Information and technology
Cloud computing is a type of Internet-based computing that provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand. It is a model for enabling ubiquitous, on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., computer networks, servers, storage, applications and services), if you need any question, please click a text button, "icon cloud"
A computer is a device that can be instructed to carry out an arbitrary set of arithmetic or logical operations automatically. The ability of computers to follow a sequence of operations, called aprogram, make computers very flexible and useful. Such computers are used as control systems for a very wide variety of industrial andconsumer devices. This includes simple special purpose devices likemicrowave ovens and remote controls, factory devices such as industrial robots and computer assisted design, but also in general purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. The Internet is run on computers and it connects millions of other computers.
Mobile computing is human–computer interaction by which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage, which allows for transmission of data, voice and video. Mobile computing involves mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software. Communication issues include ad hoc networks and infrastructure networks as well as communication properties, protocols, data formats and concrete technologies. Hardware includes mobile devices or device components. Mobile software deals with the characteristics and requirements of mobile applications.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)